In a significant economic development, India’s retail inflation plummeted to a record low of 0.25% in October 2025, down from 1.54% in September. This marks the lowest inflation reading in the current CPI series, effectively making it a 10-year low.
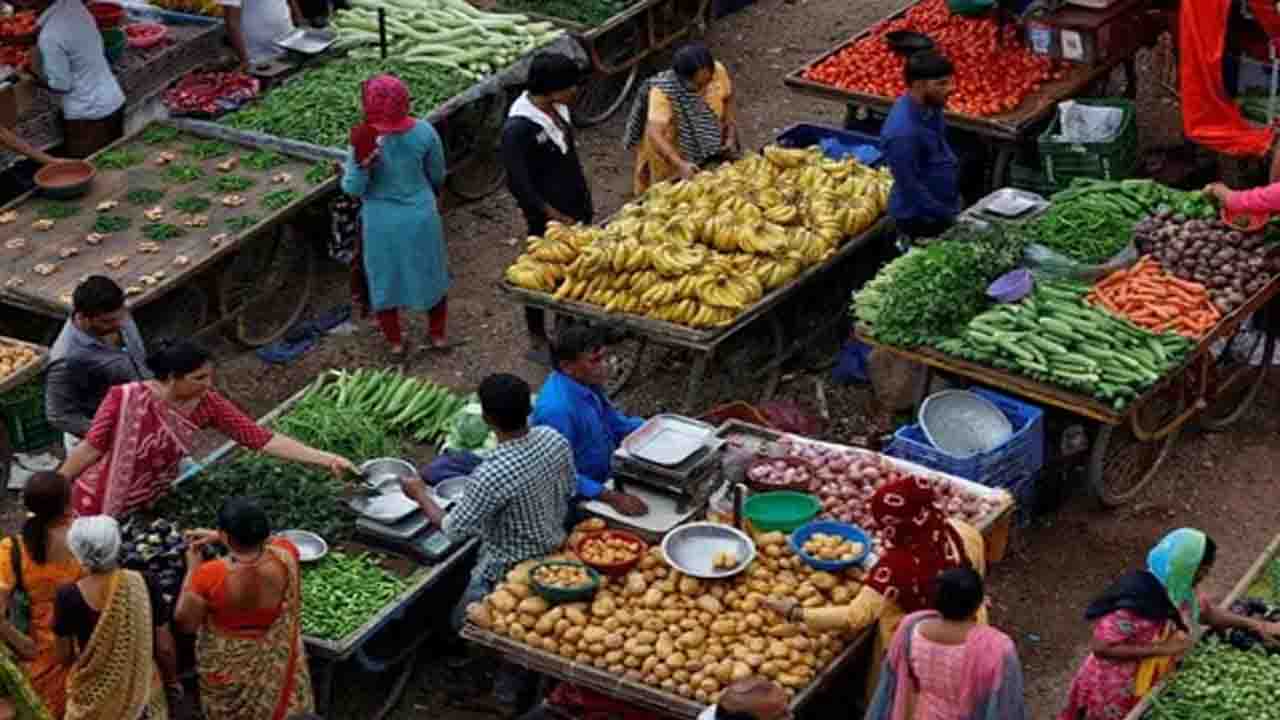
The primary driver behind this dramatic slowdown is a substantial deflation in food prices, offering major relief to common households.
Key Highlights of the Inflation Data:
-
Food Prices in Deflation: The Consumer Food Price Index (CFPI) entered deep negative territory, recording -5.02% in October compared to the same month last year. This is the lowest level in the current CPI series. The decline was steeper in urban areas (-5.18%) than in rural areas (-4.85%).
-
Rural vs. Urban: Rural India experienced deflation of -0.25%, while urban inflation cooled to 0.88%.
-
Below RBI’s Target: This is the fourth consecutive month that inflation has remained below the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) medium-term target of 4%. It has also stayed under the RBI’s upper tolerance limit of 6% for seven straight months.
-
Beats Expectations: The actual figure of 0.25% was lower than the 0.48% forecast by a Reuters poll of economists, indicating a sharper-than-expected cool-down.
What’s Causing the Slowdown?
Two major factors are at play:
-
Sharp Decline in Food Prices: A significant drop in the prices of essential food items is the most powerful factor pulling down the overall inflation number.
-
Impact of GST Reforms: The GST rate cuts, which were implemented on September 22, 2025, have started to reflect in retail prices. Reduced taxes on a range of goods, from daily essentials to vehicles, have made them cheaper for the end consumer.
What is CPI and How is it Calculated?
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) measures the average change in prices that consumers pay for a basket of goods and services. It is the key metric for assessing retail inflation.
-
Base Year: The current CPI series uses 2012 as its base year. This means the average price level of that year is set to 100. The inflation rate is calculated by comparing current price levels to this base.
-
Inflation Dynamics: Inflation typically rises when demand outpaces supply or when there is too much money chasing too few goods. Conversely, inflation falls when supply is abundant or demand is weak, as seen in the current scenario with food items.
This low inflation environment provides the RBI with more flexibility to support economic growth by potentially maintaining or adjusting its interest rate policy in the coming months.